7 Different Types of Cloud Computing Structures
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is basically a collection of different services provided by different companies.
It mainly depends on resource sharing using internet-enabled devices that allow the function of application software.
The Cloud can serve a wide range of functions over the Internet, such as storage from virtual servers, virtual applications, authorization of desktop applications, etc.
By implementing resource sharing, cloud computing is able to achieve reliability and economies of scale.
There are mainly two types of cloud computing models which are service-based and deployment based.
Cloud Deployment Models
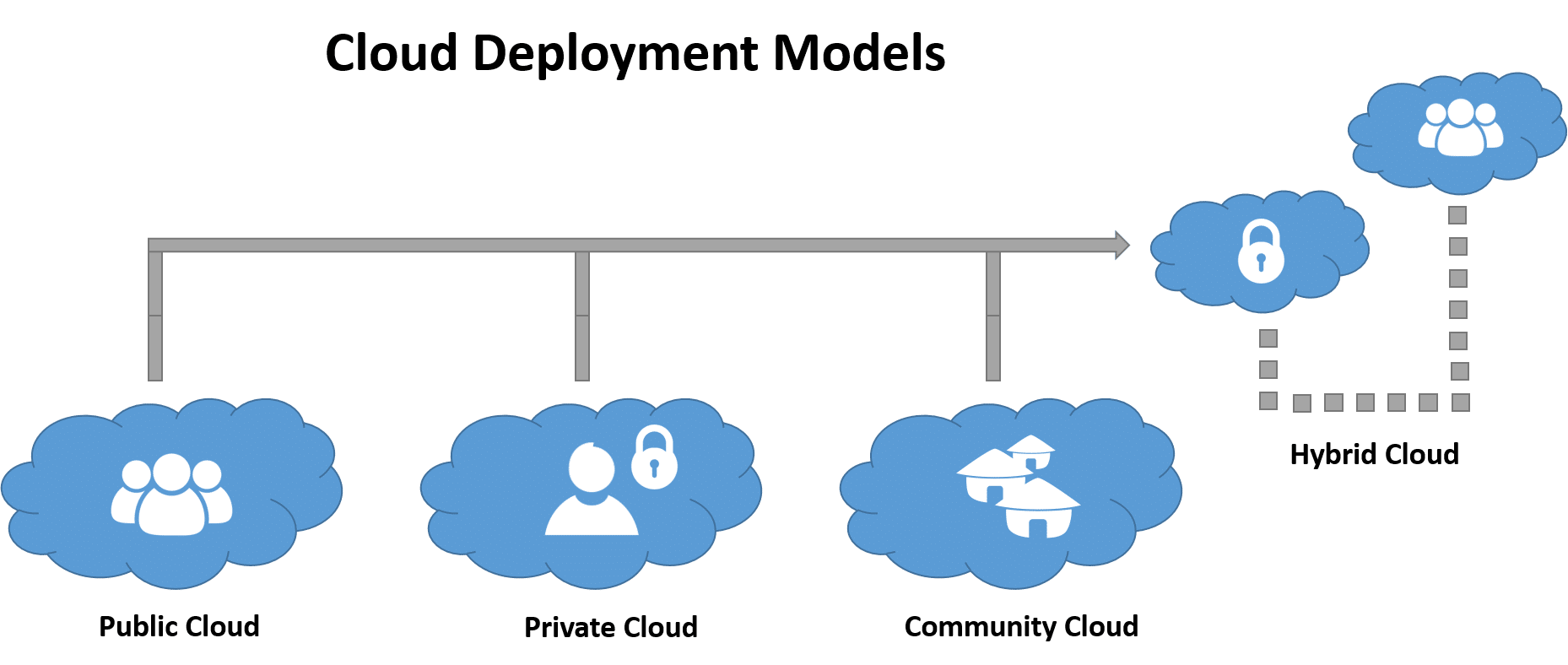
Cloud computing deployment models are based on location. In order to know which deployment model would best suit your organization’s requirements,
There are 4 types of cloud deployment models Public cloud, private cloud, Hybrid cloud, and community cloud.
Public Cloud
Public Cloud, is a type of hosting in which cloud services are delivered over a network for public use.
- Customers do not have any control over the location of the infrastructure.
- The cost is shared by all users and is either free or in the form of a license policy like pay per user.
- Public clouds are great for organizations that require managing the host application and the various applications users use.
Private Cloud
A private Cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is solely used by one organization.
- It gives organizations greater control over security and data safeguarded by a firewall and managed internally.
- It can be hosted internally or externally.
- Private clouds are great for organizations that have high-security demands, high management demands, and uptime requirements.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud uses both private and public clouds but can remain separate entities.
- Resources are managed and can be provided either internally or by external providers.
- A hybrid cloud is great for scalability, flexibility, and security.
- An example of this is an organization that can use the public cloud to interact with customers while keeping their data secured through a private cloud.
Community Cloud
It is an infrastructure that is mutually shared between organizations that belong to a particular community.
- The community members generally share similar privacy, performance, and security concerns.
- An example of this is a community cloud at banks, the government in a country, or trading firms.
- A community cloud can be managed and hosted internally or by a third-party provider.
- A community cloud is good for organizations that work on joint ventures that need centralized cloud computing ability for managing, building, and executing their projects.
Are you interested in finding out more about cloud structures and security? Check out this free whitepaper on how to ensure complete security in the cloud!
Cloud Service Models
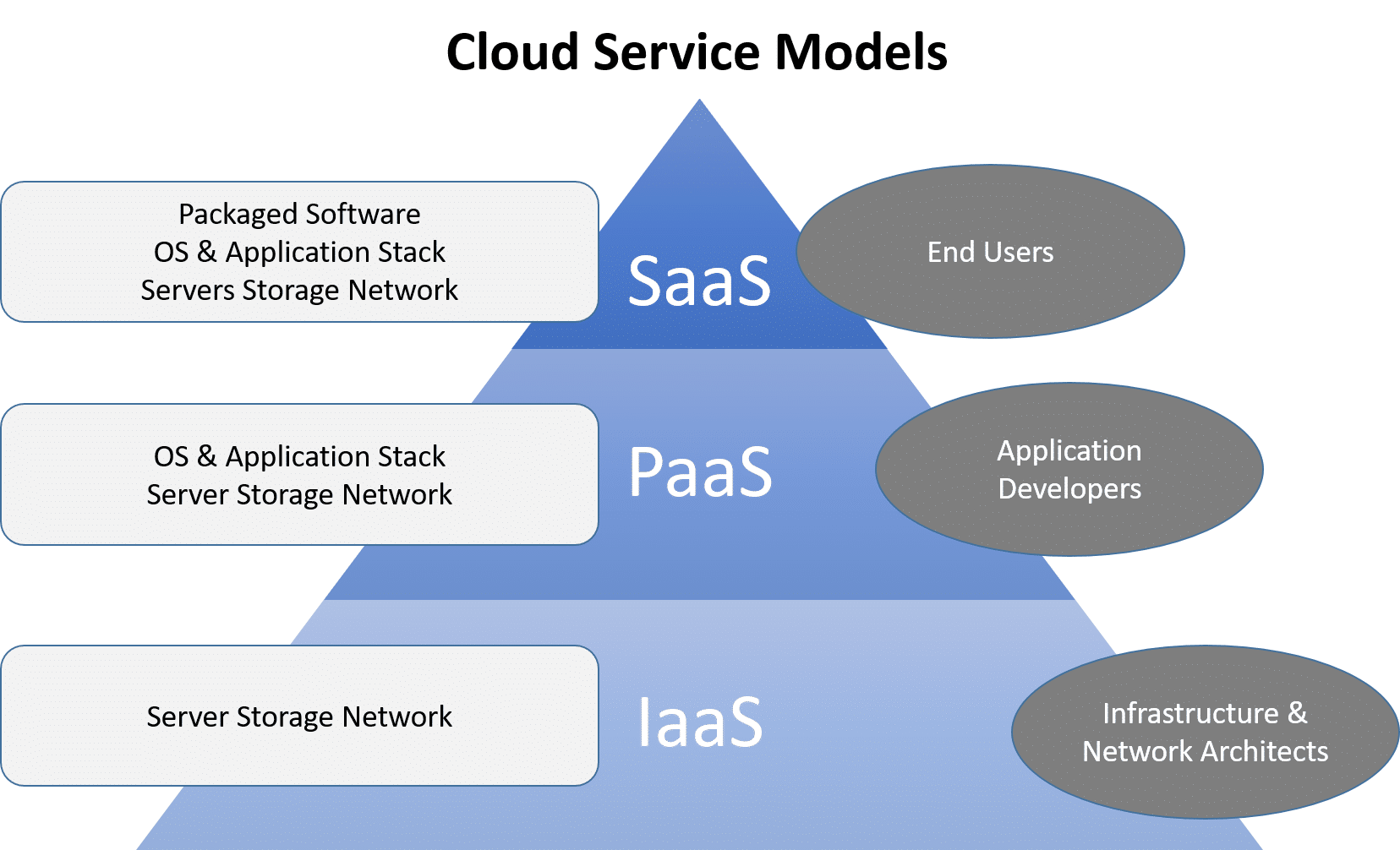
Cloud service models focus on providing some type of offering to their clients.
Cloud Software as a Service:
Cloud Software as a Service, is a type of cloud that offers an application to customers or organizations through a web browser.
- The data for the app runs on a server on the network, not through an app on the user’s computer.
- Software is usually sold via subscription
- Examples of SaaS are Salesforce, Google Docs, Office 365, Basecamp, etc.
Cloud Infrastructure as a Service
Cloud Infrastructure as a Service, provides the hardware and usually virtualized OS to their customers.
- Software is charged only for the computing power that is utilized, usually, CPU hours used a month.
- Examples of IaaS are Amazon EC2, Rackspace, Google Compute Engine, etc.
Cloud Platform as a Service
Cloud Platform as a Service, provides networked computers running in a hosted environment, and also adds support for the development environment.
- PaaS offerings generally support a specific program language or development environment.
- Deploying your app in this environment, you can take advantage of dynamic scalability, and automated database backups without the need to specifically code for it.
- PaaS is billed as an additional cost on top of the IaaS charges.
- Examples of PaaS are Google App Engine, Cloud Foundry, Engine Yard Etc.
What About Cloud Printing?
Cloud printing wirelessly connects with your computer, tablet, smartphone, and shared printers to allow you to print documents through the internet.
A major benefit to organizations using The Cloud includes sharing paper amount remote locations and not having to install a wired network.
It is extremely useful for organizations that deploy BYOD, where they let employees choose their own devices and OS.
Cloud printing offers greater convenience and improved productivity for cloud-structure industries that rely on printing.
Try UniPrint InfinityCloud
Whether you are printing at the office or at home, UniPrint InfinityCloud is the cloud printing solution of choice for your organization.
Recent Posts
- Why Traditional Printing No Longer Works In Your Office
- How to Streamline and Modernize Printing in Healthcare Environment
- When Print Management Becomes a Crisis: How to Act Fast
- 10 Ways Cloud Print Management Can Increase Security to Prevent Data Loss and Increase Productivity
- Serverless Printing 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Going Server-Free with Print
- Cloud Printing Management: The Secret to Fewer Help Desk Tickets
- Why Should You Outsource Printing Management? A Comprehensive Overview
- How Cloud Print Management Prevents Print Server Vulnerabilities
- Is Printing Dead?
- How InfinityCloud Outshines Microsoft Universal Print in 2024
- See All